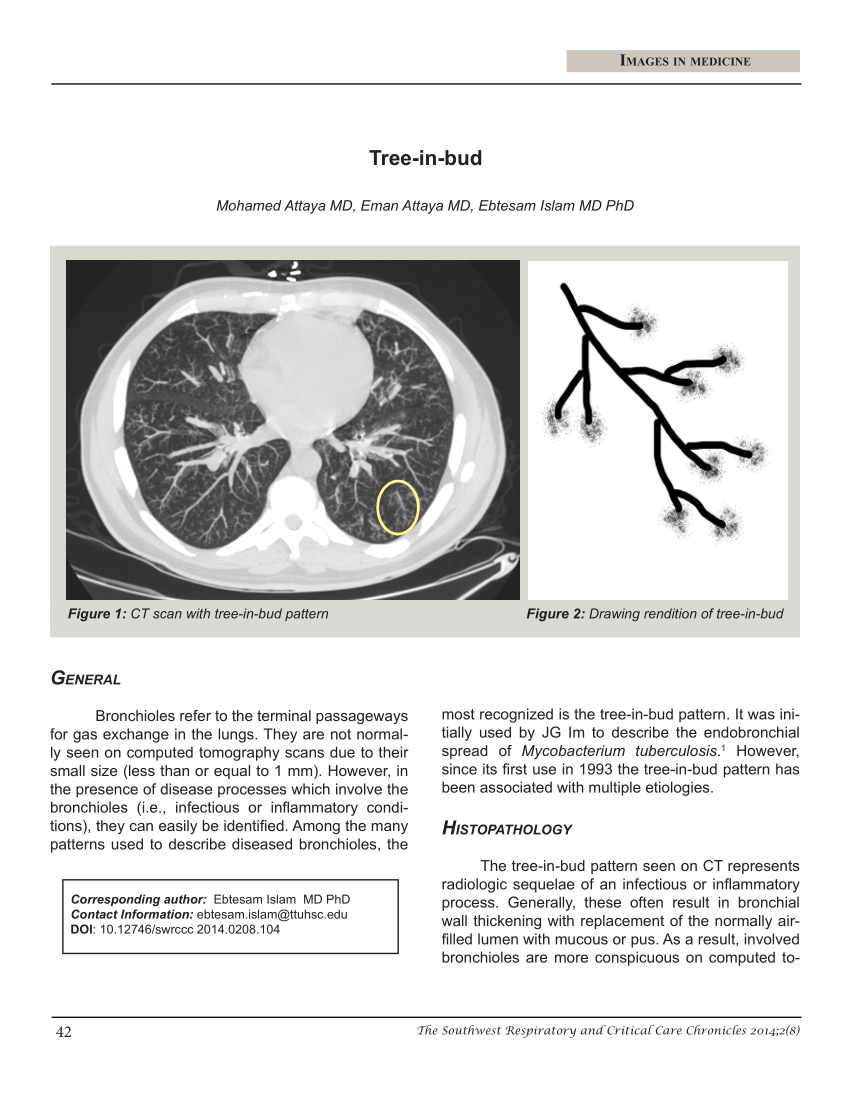
tree in bud opacities seen in
The relative frequency of tree-in-bud opacities in the clinical setting has been evaluated by Miller and Panosian. Although commonly associated with M.

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad
TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping.
. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of tib opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with tib opacities. Originally and still often thought to be specific to endobronchial Tb the sign is actually non-specific and is the manifestation of pus. CT confims numerous centrilobular nodules with opacified distal bronchioles tree-in-bud sign and bronchiectasis.
The pattern reflects a spectrum of endobronchiolar and peribronchiolar disorders including mucoid impaction inflammation fibrosis and occasionally endovascular disorders such as neoplastic processes. Simply put the tree-in-bud pattern can be seen with two main sites of disease 3. Bronchioles filled with pus or inflammatory exudate.
32 rows Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities an imaging pattern usually seen on chest CT have been reported. It is usually visible on standard ct however it is best seen on hrct chest.
Although initially described in 1993 as a thin-section chest CT finding in active tuberculosis TIB opacities are by. Distal airways more common distal pulmonary vasculature. Jennifer hong ba francisca zuazo md hanyuan shi md 1 1 tulane university la new orleans.
Relative Frequency of Tree-in-Bud Patterns in Various Diseases. Tuberculosis many infectious organisms can produce this pattern. The tree-in-bud pattern suggests active and contagious disease especially when associated with adjacent cavitary disease within the lungs.
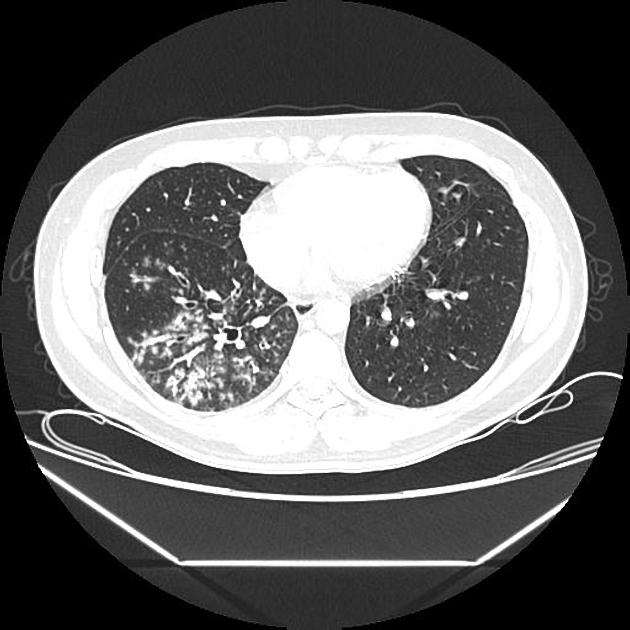
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Uncommonly this pattern can be seen in other entities that cause luminal impaction bronchiolar dilatation or wall thickening including cystic fibrosis immune deficiency inflammatory bowel disease and diffuse panbronchiolitis. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and corresponding small branches simulate the appearance of the end of a branch belonging to a tree that is in bud.
Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. Tree in bud opacities treatment. However in the presence of disease processes which involve the bronchioles ie infectious or inflammatory conditions they can easily be.
8081 On CT the tree-in-bud pattern manifests as small 24 mm centrilobular well-defined nodules connected to linear branching opacities that. Tree in bud opacities treatment. Chest x-ray in a 60 year old patient of Asian extraction demonstrates faint reticulonodular opacities.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities an imaging pattern usually seen on chest CT have been reported. It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk. It consists of small centrilobular nodules of soft-tissue attenuation connected to multiple branching linear structures of similar caliber that originate from a single stalk.
The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. 11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background. The most common causes were respiratory infections 72 including mycobacterial 39 bacterial 27 viral 3 and multiple 4 infections.
TIB opacities represent a normally invisible branches of the bronchiole tree 1 mm in diameter that are severely impacted with mucous pus or fluid with resultant dilatation and budding of the terminal bronchioles 2 mm in diameter1 photo. Found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in 256 of the CT scans in patients with bronchiectasis. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. The differential diagnosis is lengthy. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways. The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. Another important entity that can produce the tree-in-bud pattern is bronchioalveolar carcinoma BAC.
The tree-in-bud sign indicates bronchiolar luminal impaction with mucus pus or fluid causing normally invisible. However the most common process leading to this CT appearance is infection. These findings most likely represents pulmonary TB or MAC despite negative induced sputum specimens.
TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping. The tree-in-bud pattern represents centrilobular branching structures that resemble a budding tree. Bronchiectasis which may be of any cause can produce the tree-in-bud pattern.
The tree-in-bud pattern is commonly seen at thin-section computed tomography CT of the lungs. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree. The tree-in-bud pattern indicates disease affecting the small airways.
Tree in bud opacities seen in. Tree-in-bud TIB is a radiologic pattern seen on high-resolution chest CT reflecting bronchiolar mucoid impaction occasionally with additional involvement of adjacent alveoli. This is the classic appearance of the tree in bud pattern seen on chest ct.
These small clustered branching and nodular opacities represent terminal airway mucous impaction with adjacent peribronchiolar inflammation. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities an imaging pattern usually seen on chest CT have been reported. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
32 rows Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. More specifically the pattern can be manifest because of the following disease processes often in combination. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
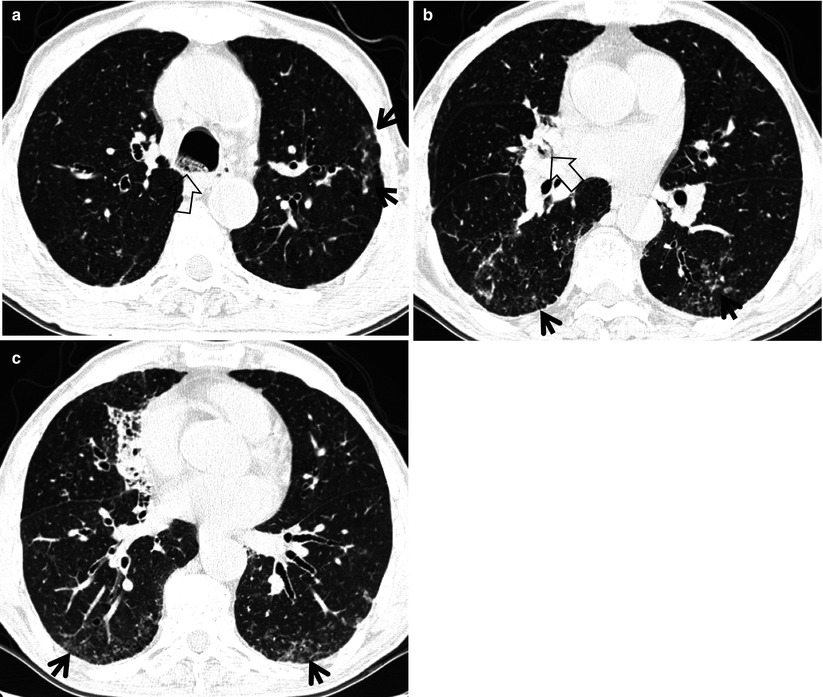
Tree In Bud Sign Radiology Key

Computed Tomography Of The Chest Showed Nodular Opacities With Tree In Download Scientific Diagram

Hrct Scan Of The Chest Showing Diffuse Micronodules And Tree In Bud Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles
2 3 Tree In Bud Pattern Seen In Both Lower Lobes Centrilobular Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Pattern Pulmonary Tb Eurorad

Tree In Bud Appearance Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

Chest Ct With Multifocal Tree In Bud Opacities Diffuse Bronchiectasis Download Scientific Diagram

Tree In Bud Caused By Haemophilus Influenzae Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Areas Showing A Mosaic Pattern Of Attenuation And Tree In Bud Opacities Download Scientific Diagram